Introduction
| The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2001 | |
||||||
|
| |||||||
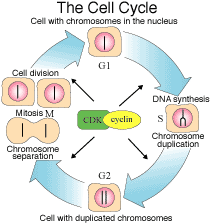 |
Organisms consist of cells that multiply through cell division. Before a cell can divide it has to grow in size, duplicate its chromosomes and separate the chromosomes for distribution between the two daughter cells. These different processes are coordinated in the cell cycle. The cell cycle consists of several phases. In the first phase (G1) the cell grows. When it has reached its appropriate size it enters the phase of DNA-synthesis (S), where the chromosomes are duplicated. During the next phase (G2) the cell prepares for division. In mitosis (M) the chromosomes separate, and the cell divides into two daughter cells. Through this mechanism the daughter cells receive identical sets of chromosomes. After division, the cells are back in G1 and the cell cycle is completed. This year’s Nobel Laureates have discovered fundamental mechanisms controlling the cell cycle. CDK and cyclin drive the cell from one phase to the next in the cell cycle. |
||||||
| Contents: | |||||||
|
|||||||
Nobel Prizes and laureates
Six prizes were awarded for achievements that have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind. The 12 laureates' work and discoveries range from proteins' structures and machine learning to fighting for a world free of nuclear weapons.
See them all presented here.
