Different prions affect different regions of the brain
|
|
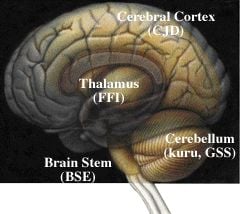 |
Cerebral cortex When the cerebral cortex is affected, the symptoms include loss of memory and mental acuity, and sometimes also visual imparement (CJD). Thalamus Damage to the thalamus may result in insomnia (FFI). Cerebellum Damage to the cerebellum results in problems to coordinate body movements and difficulties to walk (kuru, GSS). Brain stem In the mad cow disease (BSE), the brain stem is affected.
|
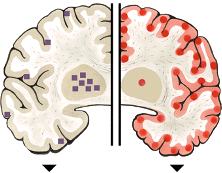
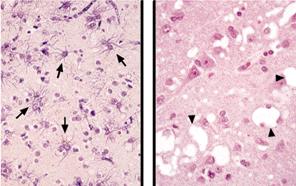
Mutations can result in different shapes of the prion protein that accumulates in different regions of the brain: In familial insomnia (FFI), mutated prions (violet squares) accumulate in the thalamus, with the result that the patients are unable to sleep. In Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, the prion protein accumulates primarily in the cerebral cortex (red dots and area).
Nobel Prizes and laureates
Six prizes were awarded for achievements that have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind. The 14 laureates' work and discoveries range from quantum tunnelling to promoting democratic rights.
See them all presented here.
